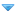
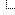Alternative formula, taking the rolling resistance of the wheels into account:
v=(P/(Cx*1,2922*A)+D^(1/2))^(1/3)+(P/(Cx*1,2922*A)-D^(1/2))^(1/3), where
v is MaxSpeed (in meters per second)
P is power after applying drivetrain losses (in watts)
Cx is drag coefficient
A is area (in square meters)
D = (((m*9,81*Cr)/(Cx*0,6461*A))^3)/27+((P/(Cx*0,6461*A))^2)/4, where
Cx, A and P are the same values as in previous formula
m is mass of the car (in kilograms)
Cr is rolling resistance for the wheels (0.01 - 0.015 for modern ordinary wheels, might be more for older ones)
It does not take the downforce into account though. However, it is relatively easy to account for it, if you want to go into such detail.
v=(P/(Cx*1,2922*A)+D^(1/2))^(1/3)+(P/(Cx*1,2922*A)-D^(1/2))^(1/3), where
v is MaxSpeed (in meters per second)
P is power after applying drivetrain losses (in watts)
Cx is drag coefficient
A is area (in square meters)
D = (((m*9,81*Cr)/(Cx*0,6461*A))^3)/27+((P/(Cx*0,6461*A))^2)/4, where
Cx, A and P are the same values as in previous formula
m is mass of the car (in kilograms)
Cr is rolling resistance for the wheels (0.01 - 0.015 for modern ordinary wheels, might be more for older ones)
It does not take the downforce into account though. However, it is relatively easy to account for it, if you want to go into such detail.